COMMERCIAL LAYER FARMING
A layer is a commercially viable egg producing bird.
Egg is in great demand because of its nutritive value, easy and quick
preparation time and as co-ingredient in wide variety of preparation
(house-hold and commercial).
Hence layer farming has gained importance as the fastest growing industry in
livestock sector.
BREED:
1.Commercial Layer Breed:
a. White Leghorn b. Kalinga Brown c. Cari Gold
d. Coloured Layer
2.Dual Purpose breed:
a. Kuroiler Dual
b. Rhode Island Red
c. Vanaraja
HOUSING & MANAGEMENT OF LAYERS
A comfortable, easy to clean and manage, providing sufficient area for the
comfort of the bird is essential requisite for getting optimum growth and
production in layer farming.
1) Away from residential or crowded areas.
2) Accessible to the market for eggs and availability of poultry feeds.
3) Well connected with roads for transportation.
4) Provision of electricity and clean water.
Requirement of a good housing
1)Well ventilated house.
3)Temperature 20°-25°C
4)Floor Concrete, rain proof, crack-free, rat-proof and easy to clean.
5)Roof- should be moist proof, and common roofing materials may be
asbestos, fibre sheet, thatch/chitra etc.
8)Height of the house 3 mts from the foundation to the roof.
2) Deep litter system: Covering of floor with litter materials like saw-dust,
rice-husk, chopped wheat straw (Depending upon the availability).
B. Back-Yard
MANAGEMENT
Brooding: is the caring of the chicks from day old till 88 weeks of age. It is
done in order to prevent chick mortality and achieve maximum growth by
providing warmth to the chicks.
Natural Brooding:
Under normal condition, the mother hen provides the chicks with the warmth
of the body and looks after the feeding too.
Artificial Brooding:
Under artificial brooding, a temperature controlled artificial brooder is used in
place of mother hen.
Following points must be followed when brooding artificially:
BROODING IN DEEP LITTER SYSTEM
Preparation before the arrival of chicks:
Sheds should be vacant for at least 3-4 weeks.
Thoroughly wash and disinfect all the walls , ceilings, floors, crevices
and equipments.
Clean all the water lines and channels.
White wash the walls of the house.
Set heating system 90 -95°F in floor brooding.
Brooder should be provided in circular fashion.
Provide clean litter material(2-4 inches deep) inside the brooder guard.
MANAGEMENT OF CHICKS IN THE BROODER (0-8WEEKS)
Provide 6 sq inches per chicks under the brooder.
Brooding should be started at 95°F temperature and be reduced by 5°F
every week until 70°F is attained.
De-beaking may be done at 3 week of age.
Provide continuous light during brooding period.
Provision of clean fresh water.
Daily inspect the condition of birds for any abnormalities.
Height of the feeder should be adjusted to the convenience of the chicks.
Keep a standby in case of emergency electricity failure.
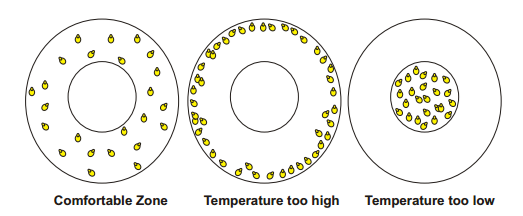
Brooding Temperature:
Patterns of chick distribution under electric brooder-
Management of Growers (9-20 weeks)
Birds should be transferred to grower house at 9 weeks of age.
Waterer and feeders should be adjusted as per the need of the birds.
Grower mash should be fed to the birds.
Keep provision for cross ventilation.
De-beaking may be done if necessary.
Vaccinate birds as per schedule.
Check feed intake and body weight at regular interval.
Provide light 12 hrs a day.
Culling of underdeveloped, diseased type of undesirable pullets as early
as possible.
Management of Layers (21-72 weeks)
Ventilation in the layer house should be adequate without drafts.
Feed layer mash to the birds.
Provide laying nest/box to the birds, use clean bedding material in the laying nest.
Replace nesting material at regular intervals.
Eggs should be collected 3-4 times a day in deep litter system of
housing.
Treatment may be made against external parasites like ticks, mites and
lice periodically.
Remove dead birds promptly and dispose them properly.
Light should start from 12 hrs a day & increased by 15-30 minutes
every week until 16 hrs of light is reached.
FLOOR SPACE REQUIREMENT
Litter Management:
Total height of the litter should be 5 cms, maintained dry, turned frequently
and treated with hydrated lime.
POULTRY FEED
As feed is the major cost of poultry production and which significantly
affects the production performance of the birds. So feed and feeding is the
most important consideration for efficient poultry farming. Improper feeding
not only affects the production performance but also causes several deficiency
diseases.
Also, the feed needs to have all the nutrients (carbohydrates, protein , fats,
minerals & vitamins) in right proportion. In addition some additives to
facilitate digestion and growth is often added in reputed commercial feed.
Estimated Feed consumption of Layers:
FEEDING SCHEDULE OF LAYER BIRDS
AT CHUJACHEN LIVESTOCK FARM
VACCINATION SCHEDULE
BIO-SECURITY MEASURES IN A LAYER FARM
Bio-security is a practice designed to prevent the spread of disease onto your
farm.
Bio-security has three major components:
Bio-security Measures
Fencing.
Keep visitors to a minimum.
Limit visits to other poultry farms.
Keep all animals and wild birds out of poultry houses.
Practice sound rodent and pest control program.
Inspect flocks daily and recognize disease symptoms.
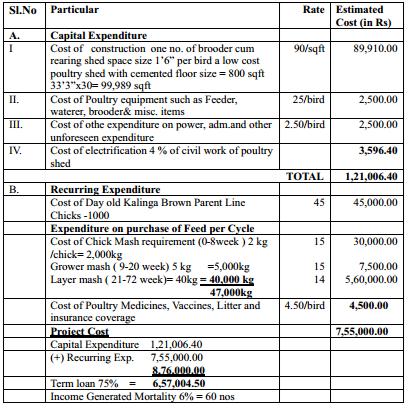
SCHEME FOR ESTABLISHMENT OF 500 NOS .OF KALINGA BROWN
COMMERCIAL LAYER FARM.
RETURNS:
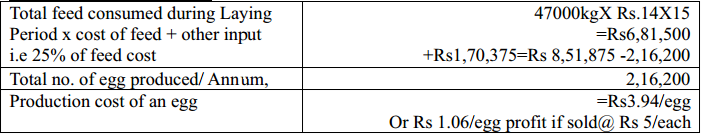
Production Cost of an egg
Calculation Table
SCHEME FOR ESTABLISHMENT OF 1000 NOS .OF KALINGA BROWN
COMMERCIAL LAYER FARM.
RETURNS:
Production Cost of an egg
Calculation Table
A layer is a commercially viable egg producing bird.
Egg is in great demand because of its nutritive value, easy and quick
preparation time and as co-ingredient in wide variety of preparation
(house-hold and commercial).
Hence layer farming has gained importance as the fastest growing industry in
livestock sector.
BREED:
1.Commercial Layer Breed:
a. White Leghorn b. Kalinga Brown c. Cari Gold
d. Coloured Layer
2.Dual Purpose breed:
a. Kuroiler Dual
b. Rhode Island Red
c. Vanaraja
HOUSING & MANAGEMENT OF LAYERS
A comfortable, easy to clean and manage, providing sufficient area for the
comfort of the bird is essential requisite for getting optimum growth and
production in layer farming.
Location of Poultry House:
2) Accessible to the market for eggs and availability of poultry feeds.
3) Well connected with roads for transportation.
4) Provision of electricity and clean water.
Requirement of a good housing
1)Well ventilated house.
2)House built in east to west direction along the long axis of the house for
natural light and sun rays.
4)Floor Concrete, rain proof, crack-free, rat-proof and easy to clean.
5)Roof- should be moist proof, and common roofing materials may be
asbestos, fibre sheet, thatch/chitra etc.
6)Light- Daylight desirable.
7)Sanitation Ease in cleaning and spraying disinfectants / sanitisers.8)Height of the house 3 mts from the foundation to the roof.
Systems of Housing
A. Intensive system (commercial)of housing includes:
1) Cage system:
2) Deep litter system: Covering of floor with litter materials like saw-dust,
rice-husk, chopped wheat straw (Depending upon the availability).
MANAGEMENT
done in order to prevent chick mortality and achieve maximum growth by
providing warmth to the chicks.
Natural Brooding:
Under normal condition, the mother hen provides the chicks with the warmth
of the body and looks after the feeding too.
Artificial Brooding:
Under artificial brooding, a temperature controlled artificial brooder is used in
place of mother hen.
Following points must be followed when brooding artificially:
BROODING IN DEEP LITTER SYSTEM
Preparation before the arrival of chicks:
Sheds should be vacant for at least 3-4 weeks.
Thoroughly wash and disinfect all the walls , ceilings, floors, crevices
and equipments.
Clean all the water lines and channels.
White wash the walls of the house.
Set heating system 90 -95°F in floor brooding.
Brooder should be provided in circular fashion.
Provide clean litter material(2-4 inches deep) inside the brooder guard.
Provide 6 sq inches per chicks under the brooder.
Brooding should be started at 95°F temperature and be reduced by 5°F
every week until 70°F is attained.
De-beaking may be done at 3 week of age.
Provide continuous light during brooding period.
Provision of clean fresh water.
Daily inspect the condition of birds for any abnormalities.
Height of the feeder should be adjusted to the convenience of the chicks.
Keep a standby in case of emergency electricity failure.
Patterns of chick distribution under electric brooder-
Waterer and feeders should be adjusted as per the need of the birds.
Grower mash should be fed to the birds.
Keep provision for cross ventilation.
De-beaking may be done if necessary.
Vaccinate birds as per schedule.
Check feed intake and body weight at regular interval.
Provide light 12 hrs a day.
Culling of underdeveloped, diseased type of undesirable pullets as early
as possible.
Management of Layers (21-72 weeks)
Ventilation in the layer house should be adequate without drafts.
Feed layer mash to the birds.
Provide laying nest/box to the birds, use clean bedding material in the laying nest.
Replace nesting material at regular intervals.
Eggs should be collected 3-4 times a day in deep litter system of
housing.
Treatment may be made against external parasites like ticks, mites and
lice periodically.
Remove dead birds promptly and dispose them properly.
Light should start from 12 hrs a day & increased by 15-30 minutes
every week until 16 hrs of light is reached.
FLOOR SPACE REQUIREMENT
Litter Management:
Total height of the litter should be 5 cms, maintained dry, turned frequently
and treated with hydrated lime.
POULTRY FEED
As feed is the major cost of poultry production and which significantly
affects the production performance of the birds. So feed and feeding is the
most important consideration for efficient poultry farming. Improper feeding
not only affects the production performance but also causes several deficiency
diseases.
Also, the feed needs to have all the nutrients (carbohydrates, protein , fats,
minerals & vitamins) in right proportion. In addition some additives to
facilitate digestion and growth is often added in reputed commercial feed.
Estimated Feed consumption of Layers:
FEEDING SCHEDULE OF LAYER BIRDS
AT CHUJACHEN LIVESTOCK FARM
VACCINATION SCHEDULE
BIO-SECURITY MEASURES IN A LAYER FARM
Bio-security is a practice designed to prevent the spread of disease onto your
farm.
Bio-security has three major components:
1. Isolation.
2. Traffic Control.
3. Sanitation.
Fencing.
Keep visitors to a minimum.
Limit visits to other poultry farms.
Keep all animals and wild birds out of poultry houses.
Practice sound rodent and pest control program.
Inspect flocks daily and recognize disease symptoms.
Good ventilation and relatively dry litter.
Keep areas around houses and feed bins clean.
No exchange of feed and equipments.
Disinfection and sanitization of poultry house & equipments.
SCHEME FOR ESTABLISHMENT OF 500 NOS .OF KALINGA BROWN
COMMERCIAL LAYER FARM.
RETURNS:
Production Cost of an egg
COMMERCIAL LAYER FARM.
RETURNS:
Production Cost of an egg
Calculation Table


















Great blog..Thanks for sharing good information. Gas Brooders that are specially designed for providing perfect temperature to birds during monsoon and winter season in the poultry farming.
ReplyDelete